How to Trade Natural Gas
Natural gas is among the most actively traded assets in the commodities market. Learn how to trade it effectively and understand the key factors that influence its price.

What is natural gas trading?
Natural gas trading involves the buying and selling of natural gas as a commodity in the global energy markets with the goal of making a profit.
Natural gas is a hard commodity (ie natural resource), which makes supply finite. As such, the natural gas price can experience significant fluctuation. This volatility makes it one of the most active and popular commodity assets among traders.
Natural gas traders typically seek to capitalise on fluctuations in the asset’s prices (ie hedging and arbitrage), driven by factors such as supply and demand dynamics, weather patterns, storage levels and geopolitical events. We explore these factors in greater detail below.
World’s biggest producers of natural gas
Over the past few decades, natural gas has become a crucial component of the overall energy landscape, supplying 23% of the world’s total energy supply. This is thanks to its growing availability, versatility and lower carbon dioxide emissions as compared to coal and oil.1
Natural gas has remained a vital fuel source for power generation, industrial processes, as well as residential and commercial heating, providing 22.3% of the world’s total electricity generation as of 2022.2
The world’s five biggest natural gas producers are:
| Rank | Top natural-gas-producing countries3 | % of total global natural gas supply |
| 1 | US | 22.4 |
| 2 | Russia | 12.3 |
| 3 | China | 8.7 |
| 4 | Iran | 6.1 |
| 5 | Canada | 3.6 |
The natural gas supply figures presented in the table above represents the sum of production and imports, minus gas that is exported or placed into storage.
Similar to oil, natural gas is extracted from reserves located deep underground or beneath the seabed. After being brought to the surface, the gas undergoes processing before being transported through pipelines to its final destinations, such as power plants and residential homes.
Over the past few decades, advancements in technology, particularly hydraulic fracturing (commonly known as ‘fracking’), have made it possible to access natural gas from sources that were once considered too costly or impractical to exploit.
What moves the price of natural gas?
The price of natural gas is a dynamic and constantly evolving reflection of the complex interplay between supply and demand forces in the energy market. As a commodity trader, understanding the key drivers that influence natural gas prices is crucial for making informed trading decisions. Let's delve into the primary factors that can cause fluctuations in the price of this essential fuel source.4
Supply dynamics
The availability and production levels of natural gas are a fundamental determinant of its price. Factors such as the number of active drilling rigs, the productivity of existing wells and the global geopolitical landscape can all impact the supply side of the equation. Disruptions in natural gas extraction or transportation, due to events like political instability, infrastructure failures or weather-related incidents, can tighten supply and drive prices higher.
Demand fluctuations
Natural gas demand is largely dictated by seasonal patterns and economic activity. During the winter months, demand typically surges as households and businesses require natural gas for heating. Conversely, during the summer, demand may increase due to the need for natural gas-fired power generation to meet air conditioning demands. Changes in industrial production, as well as the relative pricing of alternative fuels, can also influence the overall demand for natural gas.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) reported that global gas demand is expected to rise by more than 2.5% in 2024, with similar growth expected in 2025.5
Storage levels
The amount of natural gas held in storage facilities plays a crucial role in price dynamics. Traders closely monitor storage data, as low inventory levels can signal tightening supply and potential price spikes, especially during periods of high seasonal demand. On the other hand, ample storage levels can provide a buffer against supply disruptions and exert downward pressure on prices.
Weather patterns
Weather patterns can have a profound impact on natural gas prices. Extreme weather events, such as prolonged cold snaps or heat waves, can significantly increase the demand for natural gas for heating or cooling purposes, leading to price rallies. Mild weather conditions can also reduce the need for natural gas, potentially resulting in price declines.
Geopolitical and environmental factors
Government policies, emissions regulations and the global shift towards cleaner energy sources can also affect natural gas prices. Initiatives that promote the use of natural gas as a transitional fuel in the energy transition or those that restrict the production and distribution of natural gas, can influence market dynamics and pricing.
Ways to trade natural gas
You can use our CFD trading account to trade natural gas in three ways:
- Natural gas spot price
- Natural gas futures price
- Natural gas options price
Natural gas spot price
Natural gas spot trading involves the buying and selling of natural gas for immediate, ‘on the spot’ delivery, based on the current market price.
With natural gas spot CFDs (contracts for difference), you can trade based on the short-term price movements of the underlying commodity, without actually taking physical delivery.
This would enable you to get exposure to price fluctuations in the natural gas market without the logistical complexities of storing or transporting the physical commodity.
Spot trading could be particularly useful for traders looking to take advantage of near-term market opportunities and volatility.
Natural gas futures price
Natural gas CFD futures give you the ability to trade based on the future price of natural gas, by entering into a contract to buy or sell the commodity at a predetermined price and date.
CFD futures trading enables you to hedge against price risks or take a view on the long-term direction of the natural gas market.
By trading natural gas CFD futures, you can gain exposure to the commodity without the need to physically settle the contract upon expiration.
This could be beneficial for traders who want to maintain a position in the natural gas market without the associated storage and delivery obligations.
Natural gas options price
Natural gas CFD options give buyers the right, but not the obligation, to exchange underlying natural gas futures contract at a specific price (the strike price) within a certain time frame (ie set expiry date).
There are two types of options: calls and puts. If you thought the market price of natural gas was going to rise, you could buy a call option. If you thought it was going to fall, you could buy a put option. You could also sell call and put options, if you prefer to take the opposing positions.
CFD options trading potentially enables you to profit from price movements in the natural gas market while limiting your downside risk.
You could use natural gas CFD options for hedging purposes, to trade any volatility or to implement more complex trading strategies, such as spreads and straddles.
CFD options trading could be useful for traders seeking to manage risk and leverage their capital more efficiently in the natural gas market.
Natural gas trading strategies
The natural gas market is known for its inherent volatility, presenting both opportunities and challenges for traders. When aiming to capitalise on the dynamic price movements in this commodity, traders often employ a variety of strategic approaches. Let's explore three of the main natural gas trading strategies:
Day trading strategy
Day trading natural gas can be a viable strategy for traders seeking to profit from short-term price fluctuations. Natural gas prices can experience significant intraday swings, driven by factors like weather forecasts, storage reports and unexpected supply disruptions. Day traders can leverage these price movements by opening and closing positions within the same trading session, aiming to capture small but frequent profits.
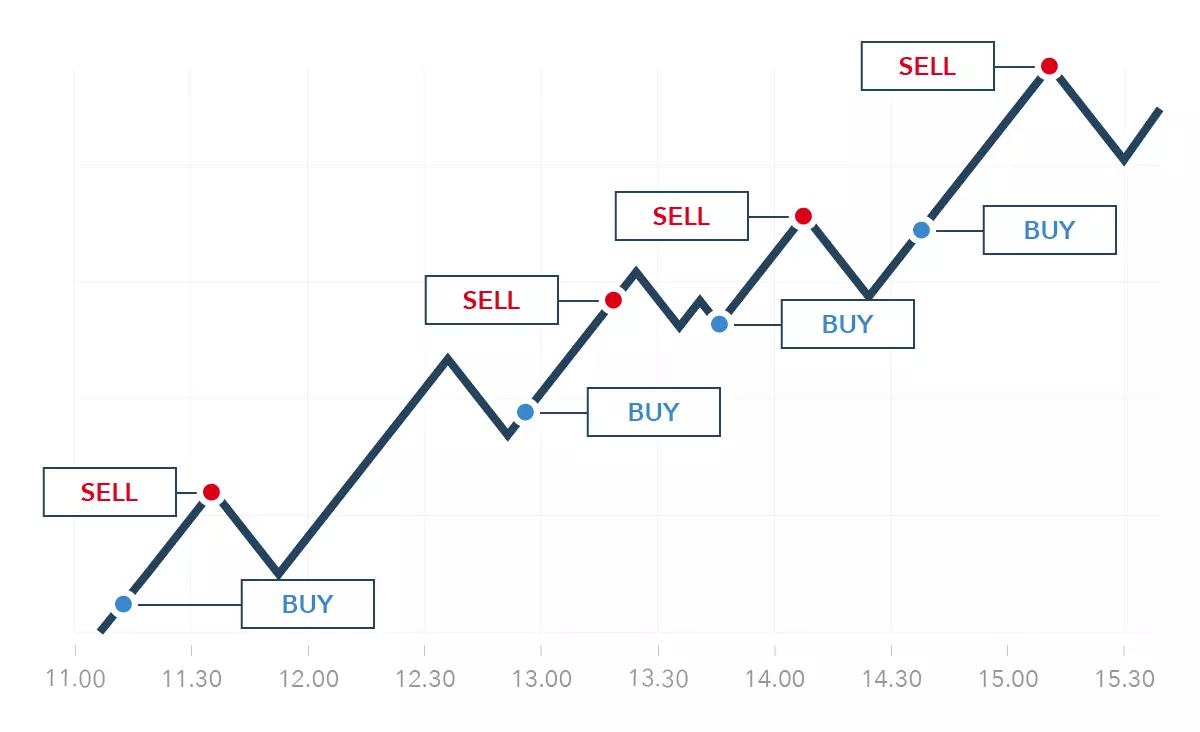
The key to successful natural gas day trading is maintaining a disciplined approach, utilising technical analysis tools, and closely monitoring market news and updates throughout the day. Traders must be able to quickly identify and react to market signals, as natural gas prices can be highly volatile and unpredictable in the short term.
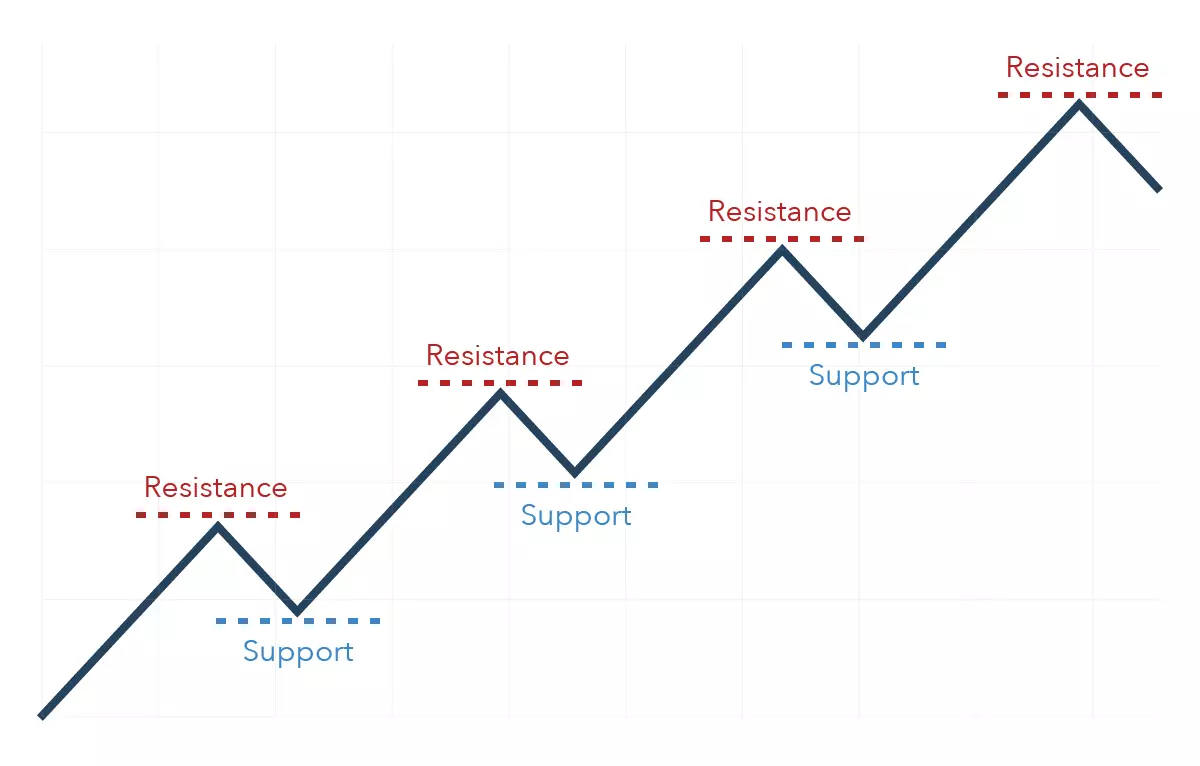
Range trading strategy
Range trading natural gas is a popular strategy in the natural gas market, as prices often oscillate within well-defined trading ranges. By identifying these price channels and executing trades accordingly, range traders can potentially profit from the market's tendency to respect established support and resistance levels.
The success of this approach depends on your ability to accurately identify reliable price ranges and execute trades with appropriate risk management measures. You must be patient and disciplined, waiting for the market to return to its established trading range before entering positions.
Breakout trading strategy
Breakout trading in the natural gas market aims to capitalise on momentum-driven market moves. When natural gas prices breach significant support or resistance levels, it can signal the start of a new trend. Breakout traders seek to enter positions as prices break out of their established trading ranges, aiming to ride the momentum of the new trend.
However, breakout trading natural gas also carries higher risk, as false breakouts (or ‘fakeouts’) can lead to volatile and unpredictable price movements. Traders must employ robust risk management techniques, such as stop-loss orders and position sizing, to navigate the inherent challenges of breakout trading.
Discover how to identify breakouts and fakeouts
Risks of trading natural gas
Trading natural gas CFDs come with the following risks and it’s crucial that you carefully manage them through proper risk management strategies, position sizing and thorough market analysis.
- Volatility: natural gas prices can experience sharp, unpredictable fluctuations, posing significant risks
- Liquidity challenges: periods of low trading volume can lead to wider bid-ask spreads and difficulty executing trades
- Leverage magnification: the use of leverage in CFD trading can amplify both profits and losses
- Regulatory changes: shifts in energy policies and emissions regulations can impact the natural gas industry and trading dynamics
- Counterparty risk: you must carefully assess the creditworthiness of your CFD provider to mitigate counterparty risk
Natural gas trading hours
| Location | Trading hours* |
| Chicago | 5pm – 4am Sunday to Friday (Central time) |
| New York | 6pm – 5am Sunday to Friday (Eastern time) |
| London | 11pm – 10am Sunday to Friday (UK time) |
* Hours are set by CME Group and may vary. Hours will shift between March and November as the UK and US change to and from daylight savings on different days
5 steps to trading natural gas
- Learn how CFDs work
- Create an account or log in and deposit your funds
- Analyse supply and demand factors in the natural gas market
- Choose the trading strategy that works best for you
- Open, monitor and close your first position
IGA, may distribute information/research produced by its respective foreign affiliates within the IG Group of companies pursuant to an arrangement under Regulation 32C of the Financial Advisers Regulations. Where the research is distributed in Singapore to a person who is not an Accredited Investor, Expert Investor or an Institutional Investor, IGA accepts legal responsibility for the contents of the report to such persons only to the extent required by law. Singapore recipients should contact IGA at 6390 5118 for matters arising from, or in connection with the information distributed.
The information/research herein is prepared by IG Asia Pte Ltd (IGA) and its foreign affiliated companies (collectively known as the IG Group) and is intended for general circulation only. It does not take into account the specific investment objectives, financial situation, or particular needs of any particular person. You should take into account your specific investment objectives, financial situation, and particular needs before making a commitment to trade, including seeking advice from an independent financial adviser regarding the suitability of the investment, under a separate engagement, as you deem fit.
Please see important Research Disclaimer.

Explore the markets with our free course
Discover the range of markets you can trade on - and learn how they work - with IG Academy's online course.

