What is margin in trading?
Did you know that you could speculate on financial markets with just a small deposit? This is called margin trading, and it could make your capital go further. Learn more about margin in trading and find out how to get started.
What is margin in trading?
Margin in trading is the deposit required to open and maintain a leveraged position using products such as CFDs and spread bets. When trading on margin, you will get full market exposure by putting up just a fraction of a trade’s full value. The amount of margin required will usually be given as a percentage.
There are two types of margin to consider when you’re trading: initial margin and maintenance margin. The initial margin is the deposit required to open the position, often called the deposit margin or just the deposit. Maintenance margin is the money that must be available in your account to fund the present value of the position and cover any running losses.
How does trading on margin work?
Trading on margin works by enabling you to open a position while only committing a fraction of the total cost upfront. The margin is determined by your trading provider’s margin system, and the amount of capital required will depend on the derivative being used and the market being traded. Markets with higher volatility or larger positions may require a bigger deposit. Margin requirements reflect your leverage. For example, if the margin requirement is 5%, the leverage is 20:1, and if the margin requirement is 10%, the leverage is 10:1.
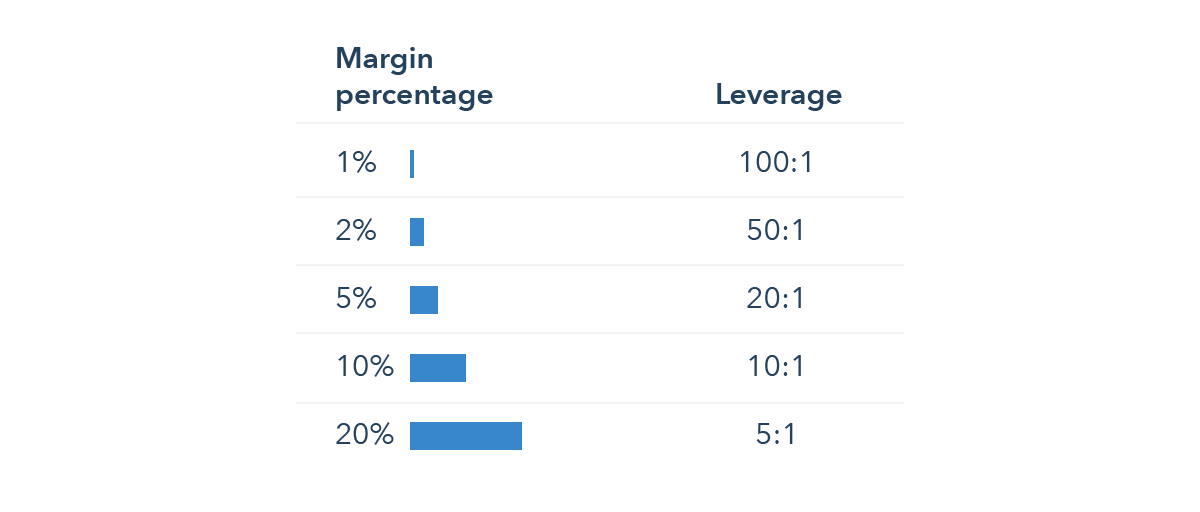
Once you have opened your position, you might need to add more money if your trade starts to incur a loss and your initial margin is no longer enough to keep the position open. If this happens, your provider will place you on margin call, and you’ll be required to top up the funds in your account – this is the additional capital known as maintenance margin.
If you’re ready to start trading on margin, open a live trading account today. You can also create a demo account to see how it works before committing your funds.
Example of buying on margin
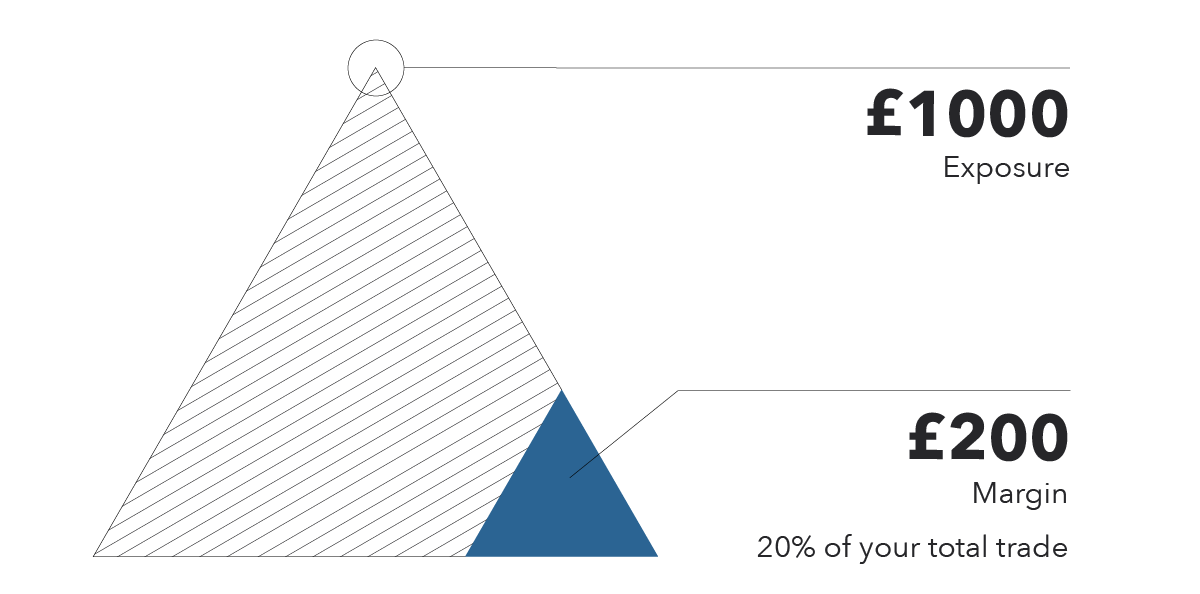
Let’s say that you want to buy £1000 worth of shares of company ABC, but you don’t want to put down the full amount. By deciding to trade on margin, you’d only need a fraction of this cost up front to get exposure to £1000 worth of shares. If your trading broker requires, for example, 20% of the position to be put forward as a margin, then the initial amount needed for the trade would be £200 (£1000 x 20%). In this example, your leverage would be 5:1.
Pros and cons of margin in trading
Pros of margin in trading
Margin can magnify your profits, as any gains on your position are calculated from the full exposure of the trade, not just the margin you put up as deposit. Buying on margin means that you have the potential to spread your capital even further, as you can diversify your positions over a wider array of markets.
Cons of margin in trading
Although margin can magnify profits, it can also amplify losses if the market moves against you. This is because your loss is calculated from the full value of the position. However, there are steps that can be taken to mitigate the negative side of margin, such as implementing a risk management strategy.
What to bear in mind before trading on margin
- Trading on margin means you only have to put down a deposit to open a position
- You could either get your deposit back and make a profit or lose it and make a loss. This will depend on whether the market moves in your favour
- The amount of margin you are required to put down depends on the asset being traded, the derivative you choose, as well as the amount of total capital you have available in your account
- Because margin increases your exposure, you have more buying power, but this could magnify both your profits and your losses
- If your margin deposit has fallen below the minimum requirement, your trading broker may notify you and you will have to fund your account immediately
- If you don’t fund your account with a maintenance margin, your positions will be closed, and you will be responsible for the loss (ie you will owe money to your broker)
- You can use risk management tools, such as stop-losses, to minimise any risk of experiencing margin call
- Always make sure you understand the margin requirements before entering a trade
What margin rates are offered by IG?
IG offers tiered margin rates, which means we apply different margin requirements at different levels of exposure. Our margin rates can range between 3.33% to 50%. If you are a professional client, you will qualify for preferential margin rates as low as 0.45%.
Here, you’ll see an example of margin rates when trading popular forex pairs with IG.
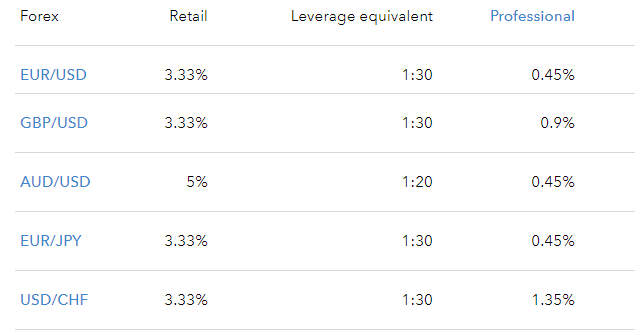
You can see a comprehensive summary of margin rates for our most popular markets here.
How to start trading on margin
To start trading on margin, follow these steps:
- Create an IG trading account or log in to your existing account
- Choose whether to spread bet or trade CFDs
- Search the asset you want to trade and select it
- Choose your position size
- Click on ‘buy’ or ‘sell’ in the deal ticket and confirm the trade
Note: When you select your position size, your margin will automatically populate at the bottom of the deal ticket.
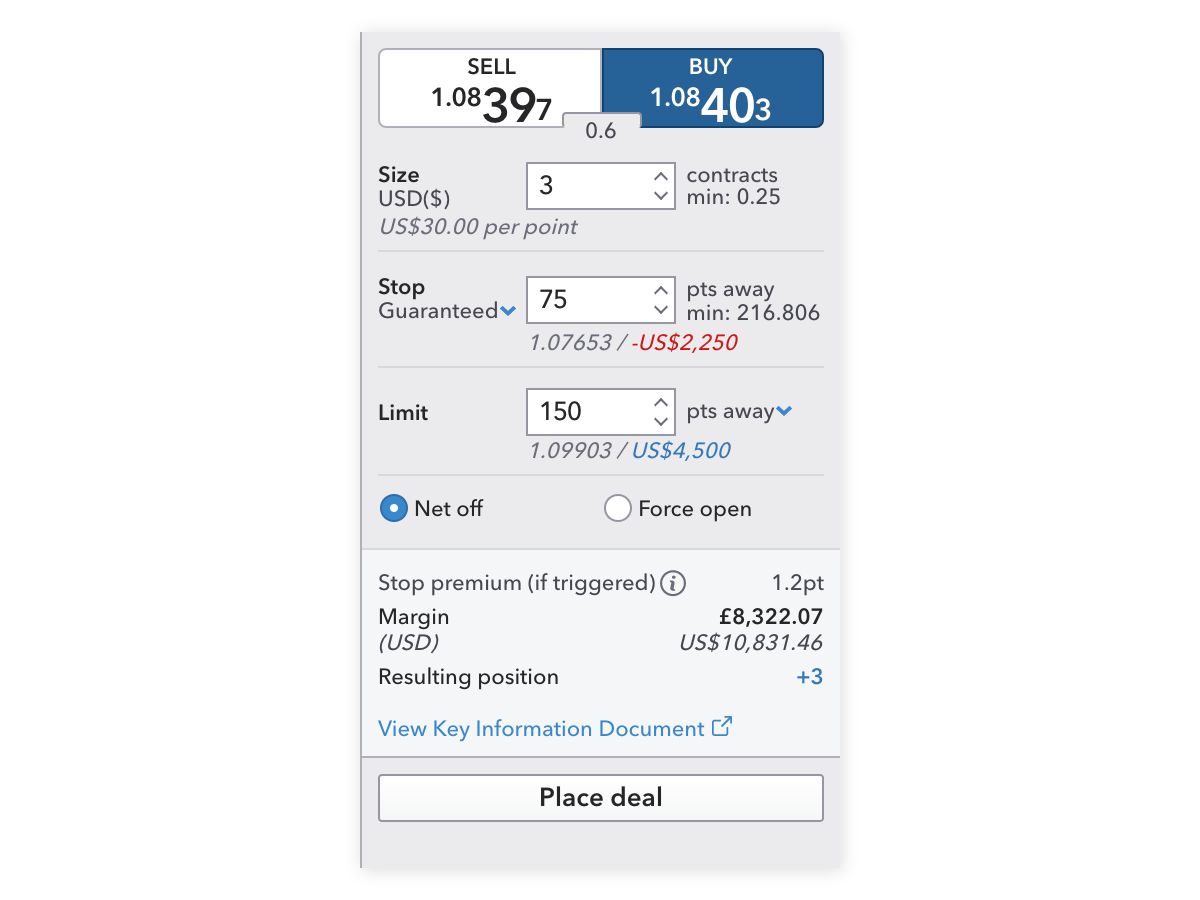
Open a live account or a demo account today.
This information has been prepared by IG, a trading name of IG Markets Limited. In addition to the disclaimer below, the material on this page does not contain a record of our trading prices, or an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument. IG accepts no responsibility for any use that may be made of these comments and for any consequences that result. No representation or warranty is given as to the accuracy or completeness of this information. Consequently any person acting on it does so entirely at their own risk. Any research provided does not have regard to the specific investment objectives, financial situation and needs of any specific person who may receive it. It has not been prepared in accordance with legal requirements designed to promote the independence of investment research and as such is considered to be a marketing communication. Although we are not specifically constrained from dealing ahead of our recommendations we do not seek to take advantage of them before they are provided to our clients.

Explore the markets with our free course
Discover the range of markets and learn how they work - with IG Academy's online course.

