With CFDs, you can lose more than you deposit, you do not have ownership in the underlying asset, and you may be subject to margin close-outs if you do not maintain sufficient margin.
What is CFD trading?
CFD trading is the method of predicting and taking a position on the price of underlying assets – like shares, indices, commodities, cryptos, forex and more – on a trading platform like ours.
A CFD – short for ‘contract for difference’ – is the type of derivative that enables you to trade the price movements of these financial markets with us.
With this form of trading, you don’t own the underlying asset – you’re only getting exposure to its price movements.
We offer over 17,000 markets for you to speculate on with CFDs, including shares, indices, forex, cryptos, commodities and more.
Some of the key characteristics of CFDs and CFD trading are explained in more detail below.

Three CFD trading essentials
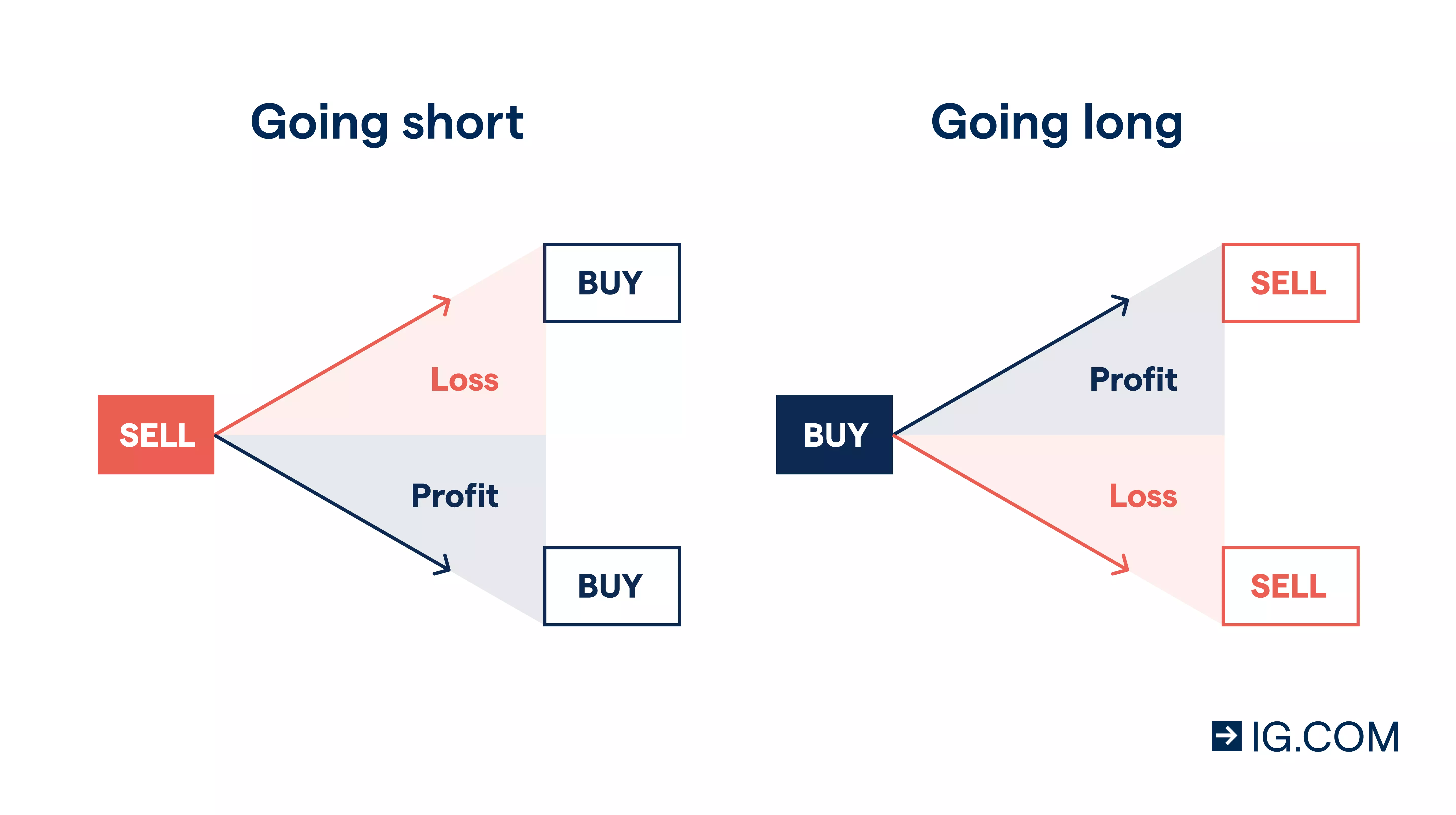
You can go long or short with CFDs
When trading CFDs, you’re predicting whether an asset’s price will rise or fall. If you think the asset’s price will go up, you’ll ‘buy’ (go long) and if you think the price will fall, you’ll ‘sell’ (go short). The outcome of your prediction will determine whether you make a profit or incur a loss.
It’s important to note that both ‘buying’ and ‘selling’ can result in a loss, and you should make sure that you understand how CFDs work before opening a position. You should also take steps to manage your risk.
To open a long CFD position in our platform, you’d choose ‘buy’ on the deal ticket and to open a short position, you’d choose ‘sell’.
CFD trading is leveraged
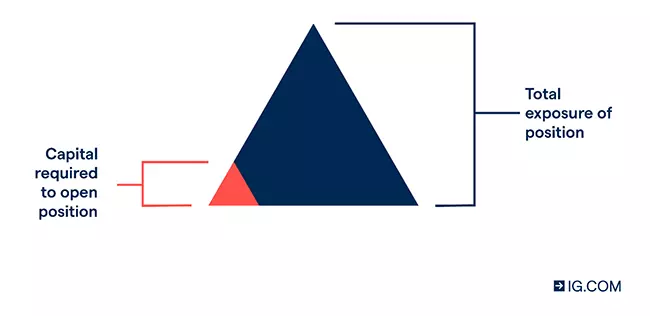
Leverage in CFD trading enables you to get full market exposure for a small initial deposit, known as margin. In other words, you only have to put up a percentage of the cost of the position as a margin, to gain exposure to the full value of the trade.
It’s important to remember that potential profits and loss will be magnified, as it will be calculated on the full size of your position – not just the margin.
For example, if you want to open a CFD trade on 50 Tesla shares, with the share price at $800 per share, you’ll only require $8000 to get exposure to a $40,000 position. That’s because your initial margin would only be 20% of the total of $40,000 trade value ($8000). But remember, your profits or losses will be calculated on the full $40,000 value of the position, not the $8000 margin.
You'll open a leveraged position with margin
CFD margin requirements can vary depending on the market that you’re looking to take a position on – and not all of our markets will have the same margin rate. For example, we require a deposit equal to 5% of the total position size on popular indices like the FTSE 100, or 20% on shares such as Tesla.
Can you trade CFDs without leverage?
When you trade CFDs with us, you’ll always be using leverage. If you don’t want to take a position with leverage, then perhaps investing will be more appealing to you. We offer share trading on over 11,000 shares and over 3000 ETFs at $0 commission per trade for Australian, US and UK shares (0.7% FX fee applies for international trades).*
*$0 commission applies to clients who trade on the IG share trading account and opt for the default setting of ‘instant currency conversion’. Clients who choose to convert currencies manually will pay commission of 2 cents per share with a minimum charge of $10 on US stocks and, for European markets, we charge £10 / €10 per trade or 0.1%, whichever is higher. Other fees and charges may apply, please see our share trading cost and charges page.
CFDs behave similarly to their underlying market
CFD trading is designed to mimic trading each underlying market relatively closely. Our CFD prices are driven by the movements of the underlying market. Some asset prices have a spread built into the buy and sell price, while other CFD trades will incur a commission – it all depends on which market you're trading.
Is CFD trading right for me?
Trading CFDs could be right for you if you’re looking for a way to trade rising or falling markets, and if you want to open a position using margin. However, CFD trading is risky, and you could make a loss greater than your initial deposit amount.
If you prefer to buy and own financial assets, share trading could be more suited to you.
We offer a demo account to all traders looking to practise their trades before opening a live account. We also give you access to IG Academy – our education tool for traders.
Why do people trade CFDs?
- Leverage: as CFDs are leveraged products, your initial outlay is only a percentage of the value of your position
- Flexibility: because you can go long or short with CFDs, you can trade no matter which way the markets are moving
- Longer hours: you can trade some markets outside of regular trading hours. Just keep in mind that the market’s opening price may differ from its out-of-hours price
- Hedging: this offers the opportunity to offset some of your losses against profits
Five steps to becoming a CFD trader
Find out how CFDs work
CFDs work by mimicking the underlying market. So, while you can mimic a traditional trade that profits as a market rises in price, you can also open a CFD position that will profit as the underlying market decreases in price.
Learn how CFD profit and loss works
To calculate the profit or loss earned from a CFD trade, multiply the deal size of your position (the total number of contracts) by the value of each contract. Then, multiply that figure by the difference in points between the price when you opened the trade and the price when you closed it.
Say, for example, that you buy 5 contracts when the asset buy price is 7500. A single contract is equal to a $10 per point, so for each point of upward movement you’d make $50 and for each point of downward movement you would lose $50 (5 contracts multiplied by $10).
As always, possible profits and losses will be magnified because these will be based on the full 7500 position, not the margin amount.
If you sell when the asset is trading at 7505, your profit would be $250
$250 = (5 x 10) x (7505 - 7500)
If you sell when the asset is trading at 7497, your loss would be $150
-150 = (5 x 10) x (7497.0 - 7500.0)
Note that these profits and losses exclude costs and charges. These could be overnight funding charges, commission or guaranteed stop fees.
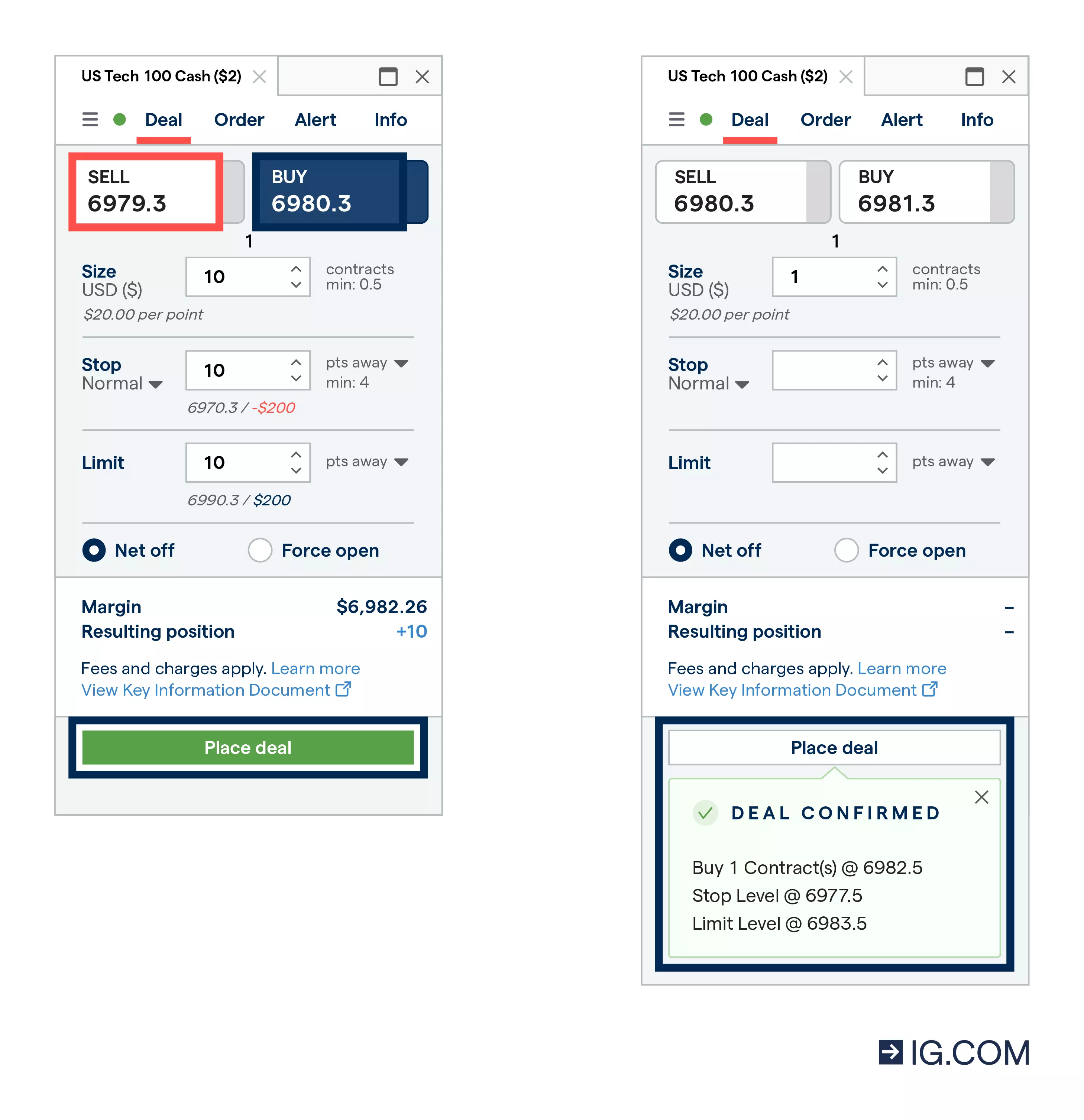
Find out how to place a CFD trade
When you’ve decided which market you want to trade, you’re ready to place a deal. If you think the value of the asset you’re trading will fall, you’d ‘sell’ (go short); if you think it will climb, you’d ‘buy’ (go long).
You can monitor all your open positions on the trading platform and close them by clicking the ‘close’ button. If you opened your position by buying, you could close by selling the same number of contracts at the sell price – and vice versa.

Learn about CFD timeframes
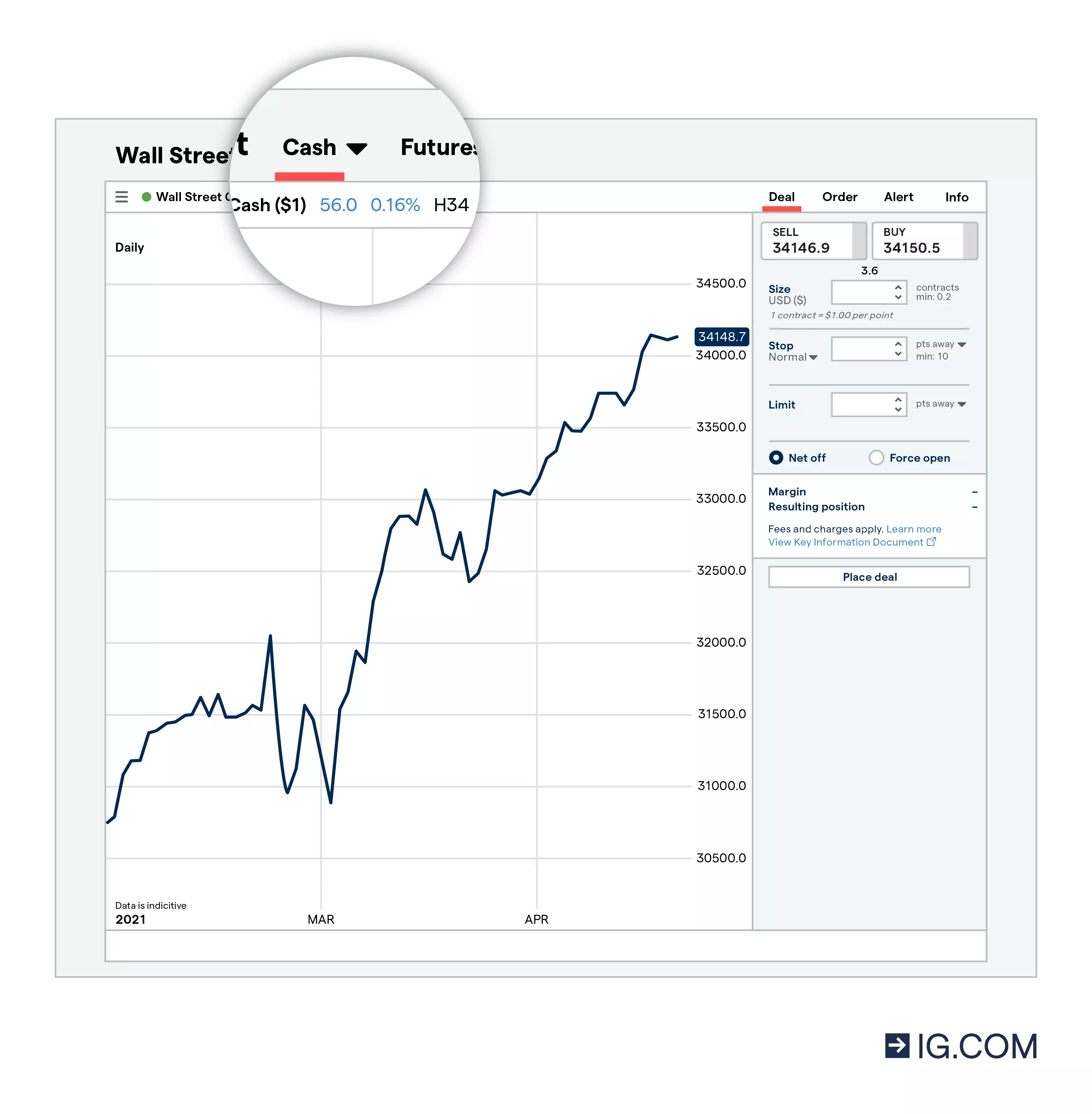
With CFDs, you can either trade the spot market or CFD futures – depending on the market that you’re looking to take a position on.
- Spot trading (also known as cash trading) is more popular for shorter-term trading, as the spot price is the immediate real-time price of the asset. We charge an overnight funding fee for spot positions that are kept open until the next day
- CFD futures are often used for medium- to longer-term trades, as they enable you to speculate on the price that underlying asset will be on a specific date. We don’t charge overnight funding on CFD futures – making it a popular choice for those who plan to keep positions open longer than a day or two
Know the costs when trading CFDs
Most of the time, the cost to open a CFD position is covered in the spread: meaning that buy and sell prices will be adjusted to reflect the cost of making the trade.
The exception to this is our share and ETF CFDs, which are not charged via the spread. Instead, our buy and sell prices match the price of the underlying market and the charge for opening a share CFD position is commission-based. By using commission, the act of taking a position on share prices with a CFD is closer to buying and selling shares in the market.
If you keep a daily CFD position open past the daily cut-off time at 9am AEDT (typically 10pm UK time, although this may vary for international markets), you’ll be charged an overnight funding charge. This is to cover the cost of maintaining your position over the longer term – as you’re trading on leverage.
Learn more about the costs for CFD trading shares and ETFs, indices, commodities, cryptos and forex.
IG Academy - free CFD trading courses and resources
Becoming a successful CFD trader takes skill, knowledge and practice. We offer everything you need to get there, with a wealth of free trading courses and webinars at IG Academy, as well as a free demo account, complete with $20,000 in virtual funds to help build your confidence.
We also offer trading strategy and news articles for all experience levels – so whether you’re a complete newcomer or a seasoned hand, we’ve got something for you.
FAQs
What does CFD mean?
CFD stands for ‘contract for difference’, a type of derivative product that you can use to speculate on the future direction of a market’s price. When trading via CFDs, you don’t take ownership of the underlying asset, which means you can take advantage of rising and falling markets by going long or short.
Learn more about what CFD trading is
How can I get started trading CFDs?
First, learn more about CFD trading via IG Academy or our demo account. Once you are confident enough, and familiar with the risks, you can open and fund a CFD account, choose which market you want to trade and do thorough analysis of the asset. When you’re ready to trade CFDs, you’ll just need to choose your position size and implement your risk management strategy.
Learn more about how to start trading CFDs
How do IG and other CFD providers make money?
The main way we make money is through the spread that we wrap around the underlying market price. The cost of trading is already factored into these two prices, called the offer and the bid, which means that you’ll always buy slightly higher than the market price and sell slightly below it.
Share CFDs are generally priced slightly differently from other CFD markets. Unlike many other CFD providers, we do not wrap our own spread on top of the market spread. Instead, we take a small commission fee when you open and close the trade.
Learn more about our charges
We do not aim to profit if a client loses, and our business model is based on providing a fair experience to all traders.
Learn more about how we make money
How do I use CFDs for hedging?
You can open a position that will become profitable if one of your other positions begins to incur a loss. An example of this would be taking out a short position on a market that tracks the price of an asset you own. Any drop in the value of your asset would then be offset by the profit from your CFD trade
To find out about using CFDs for hedging, read our guide on hedging
What is the difference between CFDs and futures?
When you trade CFDs, you buy a certain number of contracts on a market if you expect it to rise and sell them if you expect it to fall. The change in the value of your position reflects movements in the underlying market. You can close your position any time when the market is open.
Futures, on the other hand, are contracts that require you to trade on the expected future price of a financial instrument. Unlike CFDs, they specify a fixed date and price for this transaction – which can involve taking physical ownership of the underlying asset on this date – and must be purchased via an exchange. The value of a futures contract depends as much on market sentiment about the future price of the asset as current movements in the underlying market.
It’s worth keeping in mind that with us you can speculate on the price of futures contracts without buying the contracts themselves.
Does a CFD expire?
CFD positions do not have an expiry date on most markets, so can be held open for as long as you choose to maintain your position. The main CFD markets that have an expiry date are futures and options. However, overnight funding fees will be incurred if spot positions are left open after 10pm UK time (international times may vary).
Develop your knowledge of CFD trading with us
Find out more about CFD trading and test yourself with IG Academy’s range of online courses.