Margin is often required when trading the financial markets using leverage. Discover margin trading and learn how to trade on the UK’s No.1 trading platform.1

What is margin trading?
Margin trading is another term for leveraged trading – the method used to open a position on a financial market using a deposit (called margin). When trading on margin, a trading broker is essentially loaning you the full value of the trade, requiring a deposit as security.
The margin deposit is the amount of money you need to place your trade and is defined by the margin rate – which is expressed as a percentage.
For example, suppose you want to buy 10 shares valued at £100 each. If you were to buy these through a traditional broker, you’d need to pay the full £1000 upfront. At a margin rate of 20%, you’d only need to put down £200 while still getting exposure to the full value of the trade.
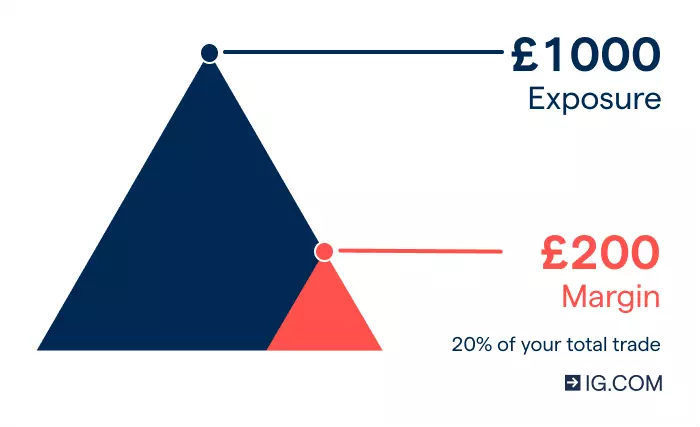
It’s important to remember that, because this initial deposit doesn’t represent your full market exposure, you could lose more than this outlay if the market moves against you. Always take steps to manage your risk.
With us, you’ll be trading on margin using financial instruments known as spread bets and CFDs. These enable you to speculate on the price movements of 15,000+ markets, including:
There are two types of margin to consider:
Initial margin
The initial margin is the minimum amount you’ll need to put up to open a position. It is sometimes called the deposit margin, or just the deposit.
Maintenance margin
The maintenance margin, also known as variation margin, is extra money that your online broker might request from you, if your position moves against you. Its purpose is to ensure you’ve got enough money in your account to always fund the present value of the position – covering any running losses
Learn more about financial markets and trading with IG Academy
How does trading on margin work?
Margin trading works by giving you full exposure to a market, but at a fraction of the capital you’d normally need to outlay. Your margin deposit is a percentage of the full position size, and the margin rate is determined by your trading provider. Markets with higher volatility or larger positions may require a bigger deposit.
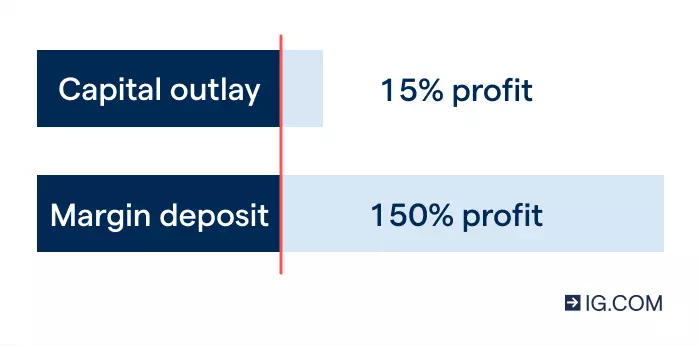
Trading on margin amplifies both profits and losses. Consider the effect of an upward £15 price change on a share worth £100. With traditional investing, this will mean that you’ve earned a 15% profit.
By comparison, at a margin rate of 10% on the same share, you’d only outlay £10 to take a position. The £15 upward price movement would now result in a profit of 150% on your initial deposit. If the price movement turned against you by £10, then you’d lose 100% of your initial deposit.
However, this magnification also works in reverse, which is why margin trading incurs increased risk over normal investing. If the share above dropped by £15 to £85, this 15% price depreciation would mean a loss of 150% on your deposit amount.
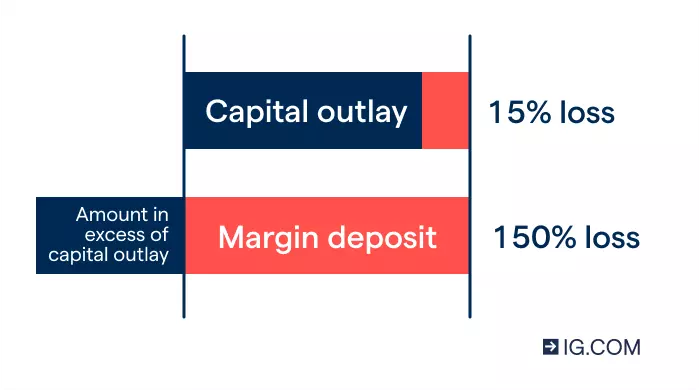
This means that while your losses are capped at your initial capital outlay with traditional investing, the same isn’t true when trading on margin. With leveraged trading you could lose more than your deposit if you don’t take steps to manage your risk.
Trading on margin example
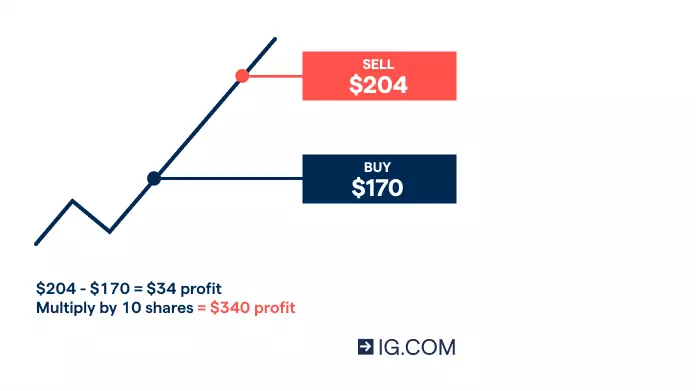
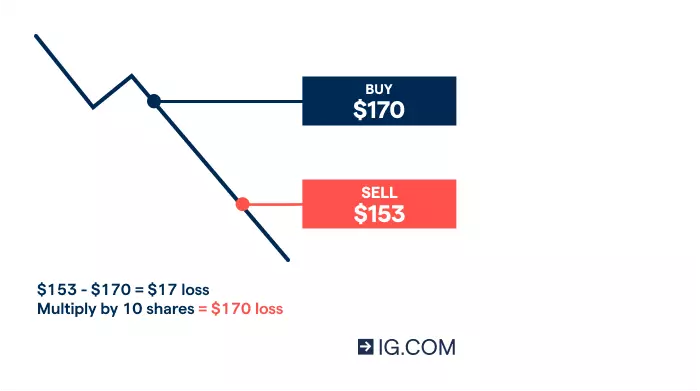
Let’s say you expect the share price of American tech giant Apple to rise due to positive news about interest rates. You decide to buy 10 shares at $170. In an unleveraged trade, this means an upfront outlay of $1700, excluding costs. By contrast, by using spread bets or CFDs, you could open your position on margin. At a margin rate of 20%, you’d only put down $340 ($1700 x 20%).
If the market moves in your favour and the Apple share price hits $204 when you sell, your profit is $34 per share, excluding costs. In this case, you’ve earned a profit of 100% on your initial margin deposit ($34 x 10 shares = $340).
Calculate profit from share CFD
On the other hand, let’s assume the market moves against you. If the share price drops by $17 to $153, your loss on the trade would be $170. This is 50% of your initial deposit, excluding costs.
Calculate loss from share CFD
What’s the difference between margin and leverage?
Margin and leverage are closely related. When you open a leveraged trade, you do so by putting down a margin deposit. This deposit gives you exposure to a larger position at a fraction of the initial capital outlay. The margin rate is expressed as a percentage, for example 10%. Leverage, on the other hand, is expressed as a ratio such as 10:1.

For a position worth £1000, depending on the market, your margin rate might be 10%. In this case, your deposit is £100. Because this deposit gives you an exposure 10 times its size, the leverage ratio is 10:1. Similarly, for a margin rate of 5%, your leverage ratio is 20:1.
Summary of our retail margin requirements and leverage ratios*
| Retail margin | Leverage equivalent | |
Forex |
3.33% |
1:30 |
Indices |
5% |
1:20 |
Shares |
20% |
1:5 |
Commodities |
5% |
1:20 |
* These margin rates may not be applicable to all assets. See our margin rates for all markets.
Benefits and risks of margin in trading
Benefits of margin
Margin can magnify your profits, as any gains on your position are calculated from the full exposure of the trade, not just the margin you put up as deposit. Buying on margin means that you have the potential to spread your capital even further, as you can diversify your positions over a wider array of markets.
Risks of margin
Although margin can magnify profits, it can also amplify losses if the market moves against you. This is because your loss is calculated from the full value of the position. However, there are steps that can be taken to mitigate the negative side of margin, such as implementing a risk management strategy.
If you’re ready to start trading on margin, open a live trading account today. You can also create a demo account to see how it works before committing any funds. Alternatively, if you’d like to buy and own shares instead of trading on margin, consider our share dealing offering.
What is a margin call?
A margin call is the alert we aim to send if the capital in your trading account has fallen below the minimum amount needed to keep a position open. A margin call can mean that you’d need additional funds to balance the account, or to close positions to reduce the maintenance margin required.
Example of maintenance margin and margin call
Let’s say you want to go long on 1000 shares of mining giant Glencore, which are currently trading at 500p. This means that the full value of your position is £5000. However, because you’re trading on leverage, you only need to put up an initial deposit of 20%. Your margin deposit is therefore £1000 (£5000 x 20%).
You have £1000 in your account when you decide to place the trade, which is enough to cover your initial margin requirement. But if the money in your account falls, due to your loss-making position, you’d immediately be placed on margin call. This is because you don’t have any additional funds with which to cover your losses.
To keep your position open, you’d need to top up your account to get your balance above £1000. The amount of money you’d be required to deposit is your maintenance margin. If your balance fell to £980, for example, you’d need to add £20 to your account.
1. Learn how margin trading works
You can access plenty of free resources on this website and on IG Academy. These resources will help you have a better understanding of how financial markets work. You can also learn how trading on margin works and familiarise yourself on the associated risks.
2. Decide how you want to trade on margin
When trading with us, you’ll be using leveraged derivatives known as spread bets and CFDs to trade on margin. Through these financial instruments, you can track the price movement of the underlying markets.
3. Create an account
Open a live trading account with us. You’ll be required to fill out a short form before we verify your identity. Once this has been successfully completed, you can deposit funds into your account and start trading.
If you’re not ready to trade or you’d like to boost your confidence as a trader, you can open a demo account. You’ll have access to £10,000 in virtual funds to practise in a risk-free platform.
4. Find your opportunity
Choose which of the 15,000+ popular markets you’d like to take a position on when trading on margin. Some of these markets include shares, forex, commodities, and indices.
5. Place your first trade
Once you’ve completed the above , you can set your position size. Remember to take the necessary steps to manage your risk, then place your deal and monitor its price movements.
FAQs
What is margin trading?
Margin trading is when you put down a deposit to open a position with a much larger market exposure. Your broker will then credit your account with the full value of the trade. This will need a deposit – known as margin – as security.
What is a margin deposit?
A margin deposit is the amount you’ll need to place your trade. It’s defined by the margin rate, which is expressed as a percentage.
What is maintenance margin?
The maintenance margin is an extra sum of money your online broker might request from you if the position you’ve taken moves against you. The money ensures there’s always sufficient funds available to finance the present value of the position. It also covers any running losses you might incur.
What is a margin call?
A margin call is when the total funds you’ve deposited onto your account, plus or minus any profits or losses, drops below your margin requirement. Your positions become at risk of being automatically closed in order to reduce the margin requirement on your account.
You can correct this by either depositing enough funds to increase the equity in your account above the margin requirement, or reduce it by closing your positions.
Is leverage the same as margin?
Leverage isn’t the same as margin, but they’re closely related. When you open a leveraged trade, you’ll put down a margin deposit. This deposit increases your exposure to the full value of the underlying asset at a fraction of the initial capital outlay.
Try these next
We’ll help you understand your trading needs
Learn how to trade using our award-winning platform
Explore our resources and take your trading skills to the next level
1 Awarded ‘best finance app’, ‘best multi-platform provider’ and ‘best platform for active traders’ at the ADVFN International Financial Awards 2022.
