Spot trading enables you to get exposure to thousands of assets via our cash markets. Use this guide to find out how to trade commodities, forex, shares, indices and more on the spot. Interested in trading our spot markets?
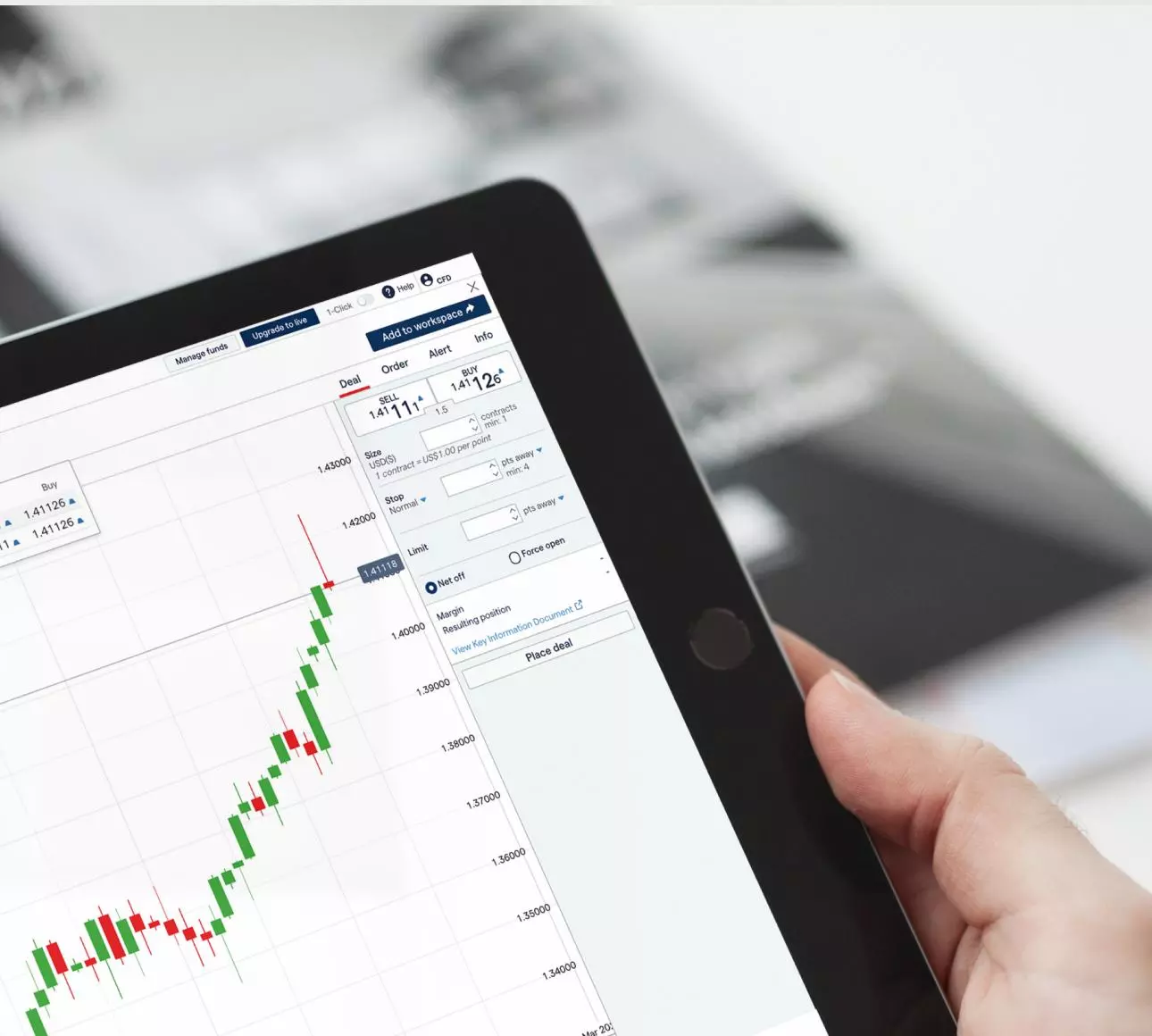

Steps to trading spot markets
What is spot trading?
Spot trading is the method of buying and selling assets at the current market rate – called the spot price – with the intention of taking delivery of the underlying asset immediately. Spot market trading is popular among day traders, as they can open short-term positions with low spreads and no expiry date.
With us, you can trade the spot market, also called the cash or undated market, via derivatives such as spread bets and CFDs. You don’t have to take ownership or delivery of the assets, and you’ll benefit from real-time, continuous pricing that reflects the underlying market. Plus, you can open a position using a deposit (margin), which increases your exposure to the market, potentially leading to magnified profits. However, this can also lead to amplified losses.
For example, if you think the price of silver is going to increase, you will buy the spot silver market (go long). If the silver price increased, you would make a profit, but if it decreased, you would make a loss.
Trading on the spot is just one of the ways you can get exposure to financial markets using derivatives. If you’re interested in longer-term positions, you could consider options trading, futures trading or forwards.
Learn why people trade spot (cash) markets
You may be interested in spot markets because:
- You can trade on the spot with continuous, real-time pricing
- Spot prices reflect the underlying market
- You can access some of the lowest spreads in the UK – starting at 0.3 points
- There are no fixed expiries on spot positions
- You can benefit from continuous charting, which could be helpful when conducting technical analysis
- It’s good for short-term trading, as there are no expiries on positions
- You can trade using leverage, opening positions using margin. Remember that while this can amplify profits, it also has the potential to magnify losses
Pick a spot market to trade
Choose from thousands of financial markets, including:
- Forex, with major pairs such as GBP/USD and EUR/USD
- Commodities, including oil, gold and silver
- Shares, such as Apple, BP and Barclays
- Indices, including the FTSE 100, Germany 40 and US 500
- ETFs, including iShares Core S&P 500 ETF and the Vanguard FTSE 100 UCTIS ETF
Please note that spot markets are referred to as ‘spot’ or ‘cash’ on our platform.
Create a spot trading account and log in
It only takes a few minutes to open an account and you can do it online. You can trade spot markets using a spread betting or CFD trading account. There’s no obligation to add funds until you want to place a trade.
Open a trading account with us to start trading spot markets
Alternatively, you could practise trading in our risk-free demo account.
Find your spot trading opportunity
To find a good spot trading opportunity, it is important that you follow news and economic events, and keep an eye on your target price levels using technical and fundamental analysis. Once you’ve opened an account with us, you can start making the most of the exclusive tools you’ve got at your disposal, including:

Expert analysis
Get technical and fundamental analysis from our analysts

Technical indicators
Discover price trends using our in-platform tools such as MACD and Bollinger bands

Trading alerts
Know as soon as your target price is met with our automated trading alerts

Trading signals
Receive actionable ‘buy’ and ‘sell’ suggestions based on analysis
Decide whether to go long or short
When you trade derivatives, you can take advantage of spot markets that decline in price (known as going short, or short-selling), as well as those that increase (known as going long). This is because you are speculating on an asset’s price, rather than buying the underlying asset itself.
If you expect the value of an asset to go up, you’d buy to go long, and if you expect if to fall, you’d sell to go short. Your profit or loss will depend on the outcome of your prediction.
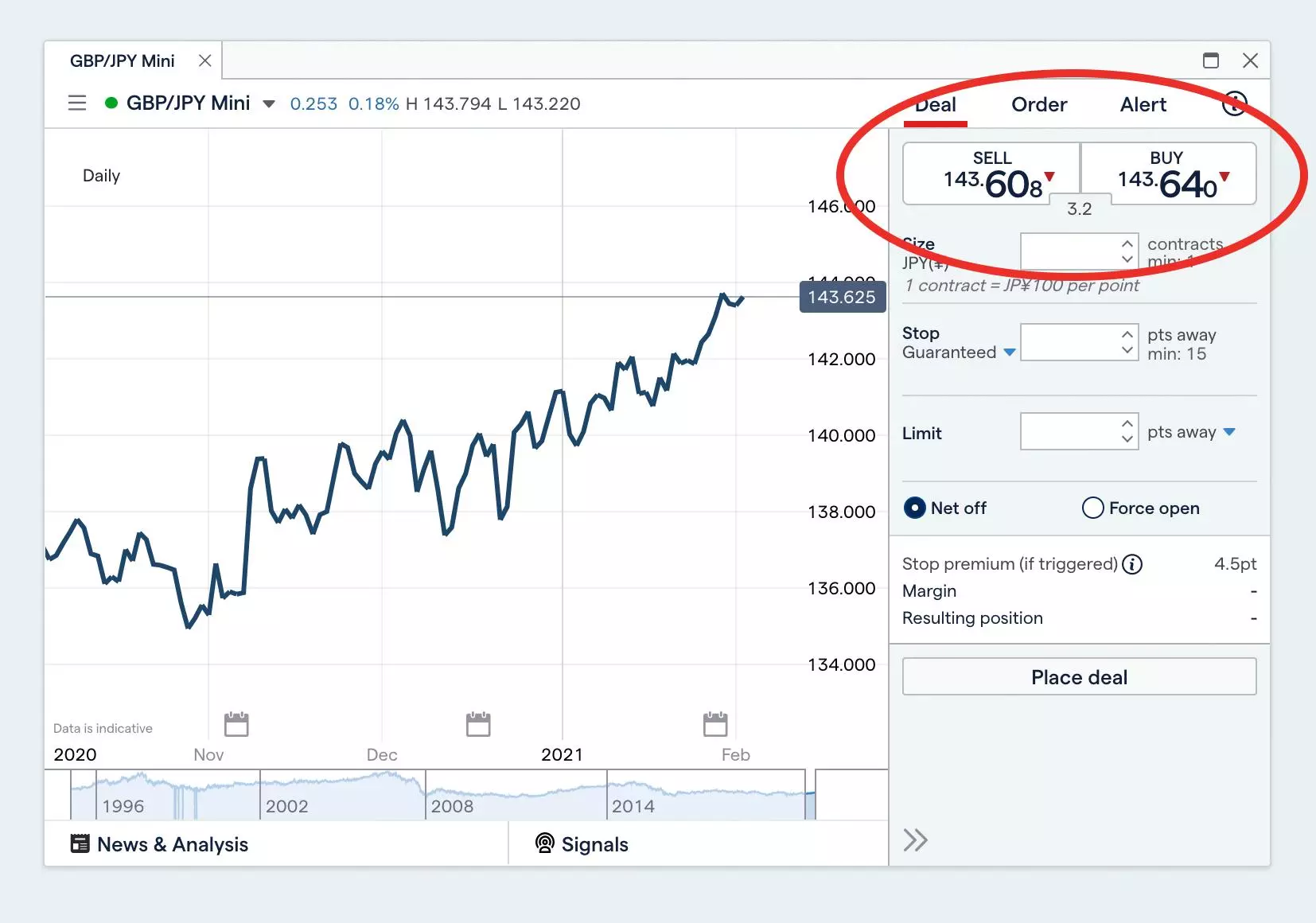
Set your stops/limits and place your trade
You can attach stops and limits to your open positions on our spot trading platform. These can help you mitigate your risk by minimising losses and securing profits.
You can choose between basic, guaranteed and trailing stops, which will close out your position if the market moves in an unfavourable direction. However, note that a basic stop can incur slippage if there are large movements or gaps in the market.
Limits do the opposite to stops – they close your position when the market moves a specified distance in your favour.
.jpg/jcr:content/renditions/original-size.webp)
Monitor and close your position
You can monitor your open positions on your IG account. Any running profit or loss will move in line with the underlying asset prices. Once you are ready to close your trade, click on the open position and select the ‘close’ button. Your final profit or loss would be realised upon the closing of the trade – the calculation would vary depending on whether you are trading CFDs or spread betting.
Remember to follow your trading plan when closing positions, and avoid emotional trading decisions such as fear or greed.
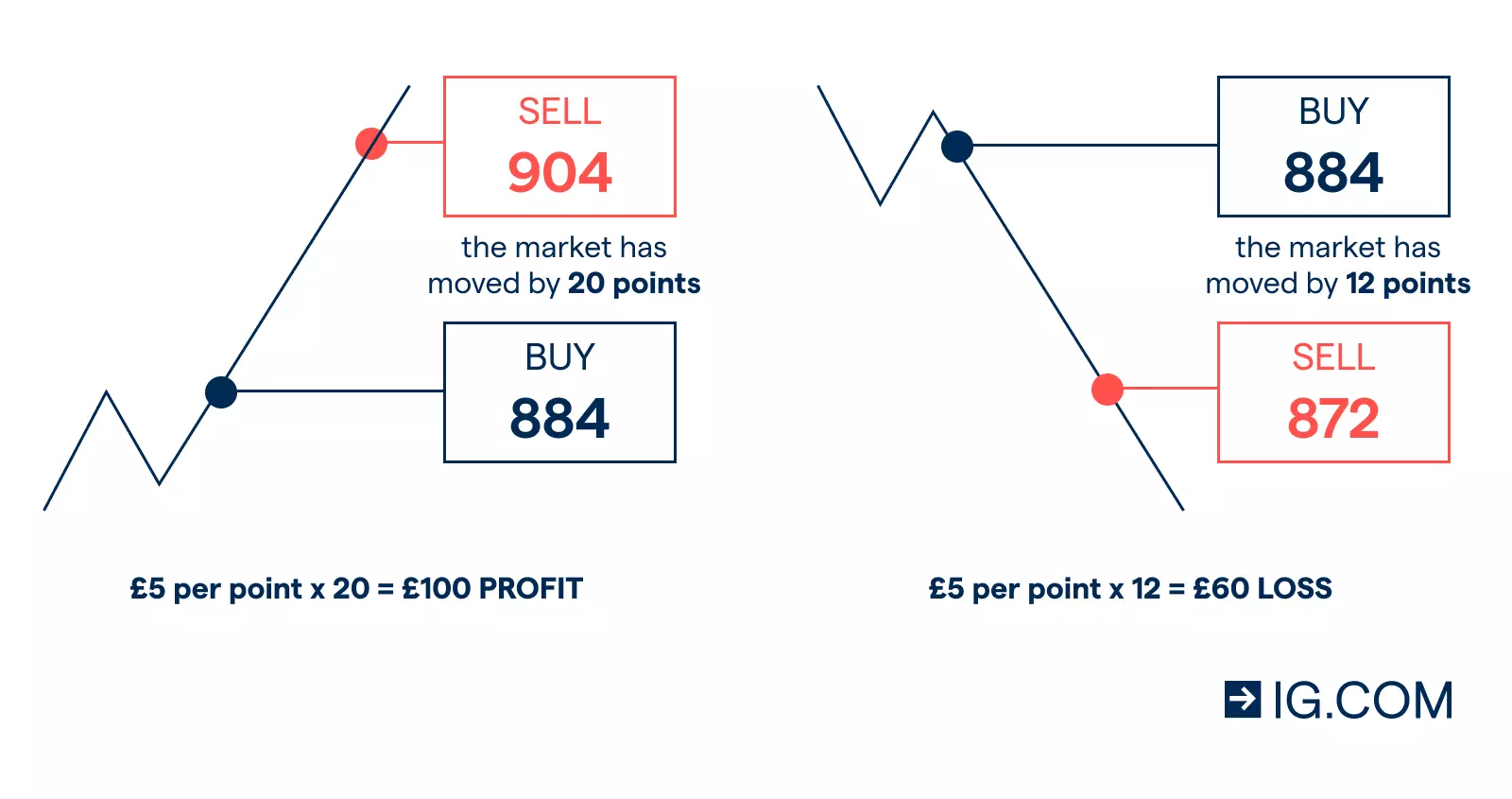
See a spread betting example
Let’s say you expect the Tesla share price to rise from 885 over the next couple of days. You open our spread betting platform and you see that the buy price is 884 and the sell price is 886. You could open a spread betting position to buy the market at £5 per point of movement. Every point of movement in the underlying market is now worth £5 to you – so if the Tesla share price rises by 20 points, you’d make a £100 profit but if it falls by 12 points, you’d make a £60 loss.
Alternatively, if you thought the Tesla share price would fall, you could open a spread bet to sell the market. If it did fall in price, you’d profit – but if it increased instead, you’d make a loss.
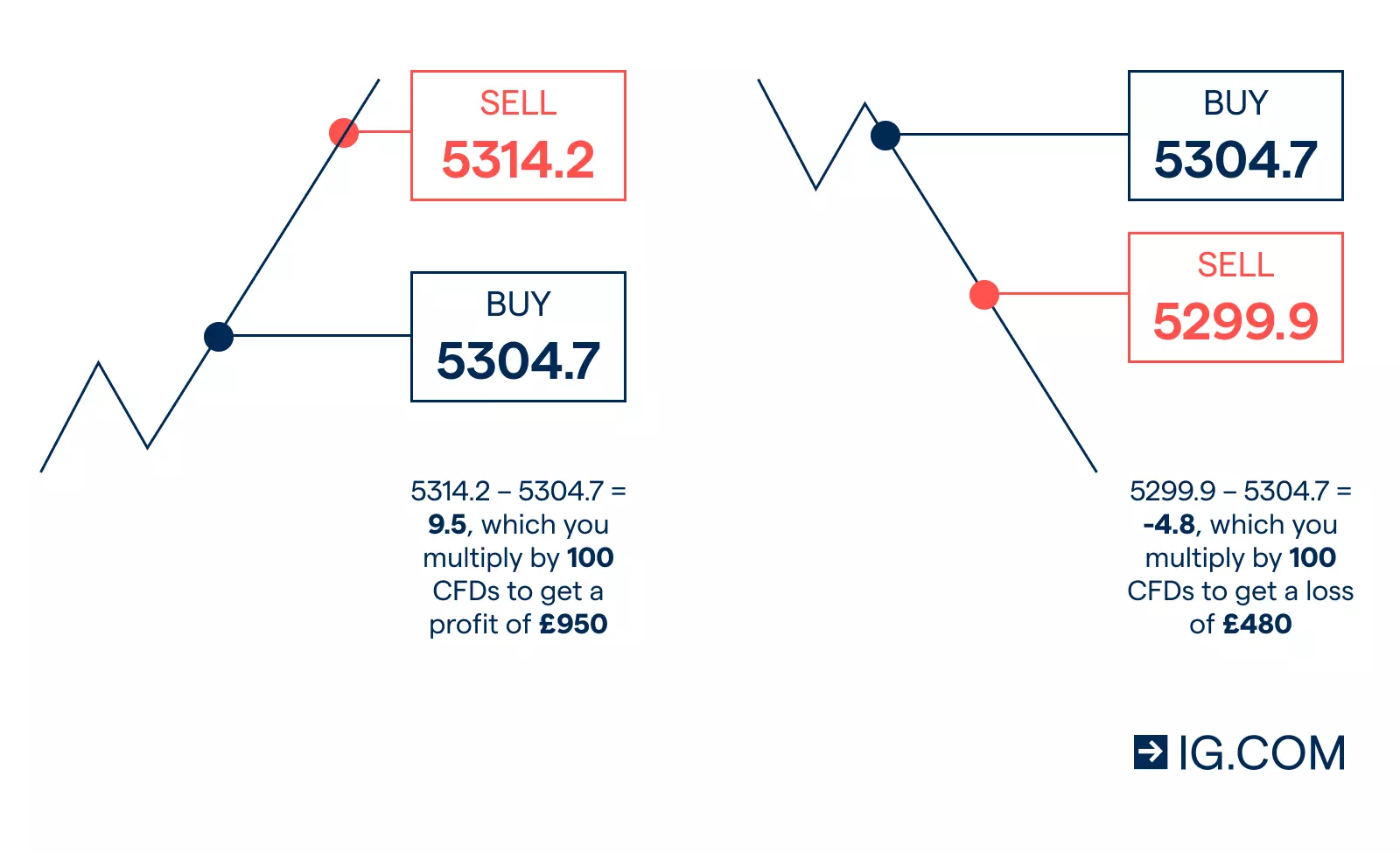
See a CFD example
Say oil has an underlying market price of 5314.6, with a CFD sell price of 5324.5 and a CFD buy price of 5304.7. You think the oil price will go up, so you buy 100 CFDs, equivalent to 100 barrels of oil, at 5304.7. If your prediction is correct, you’ll make a profit, but if it is incorrect, you’ll incur a loss.
To calculate your profit or loss, you’ll multiply the difference between the closing price and the opening price of your position by its size.
FAQs
What is the definition of a spot market?
A spot market is a financial market where you can buy and sell assets at spot prices, which reflect the underlying asset’s price. There are no fixed expiries on spot trades and you can open short-term positions, which makes spot trading popular among day traders. With us, you’ll trade the spot market via spread bets or CFDs, which means you don’t have to take ownership or delivery of the assets.
What’s the difference between spot, cash and undated markets?
There is no difference between spot, cash and undated markets – these are simply different names for the same type of market.
How can I trade spot markets?
You can trade spot markets via derivatives such as spread bets and CFDs. You don’t have to take ownership or delivery of the assets, and you’ll benefit from real-time, continuous pricing that reflects the underlying market. Plus, you can open a position using just a small deposit (margin), which can magnify your profits if your trade is successful. However, it can amplify losses if the market moves against you.
What markets can I trade on the spot?
You can trade almost any market on the spot, including forex, shares, indices, commodities and ETFs.
Try these next…
Discover everything you need to know about what spread betting is and how it works.
Learn about trading contracts for difference (CFDs) and see an example of how it works.
Find information on trading futures contracts and see which markets are available.
