Quote price definition
What is a quote price?
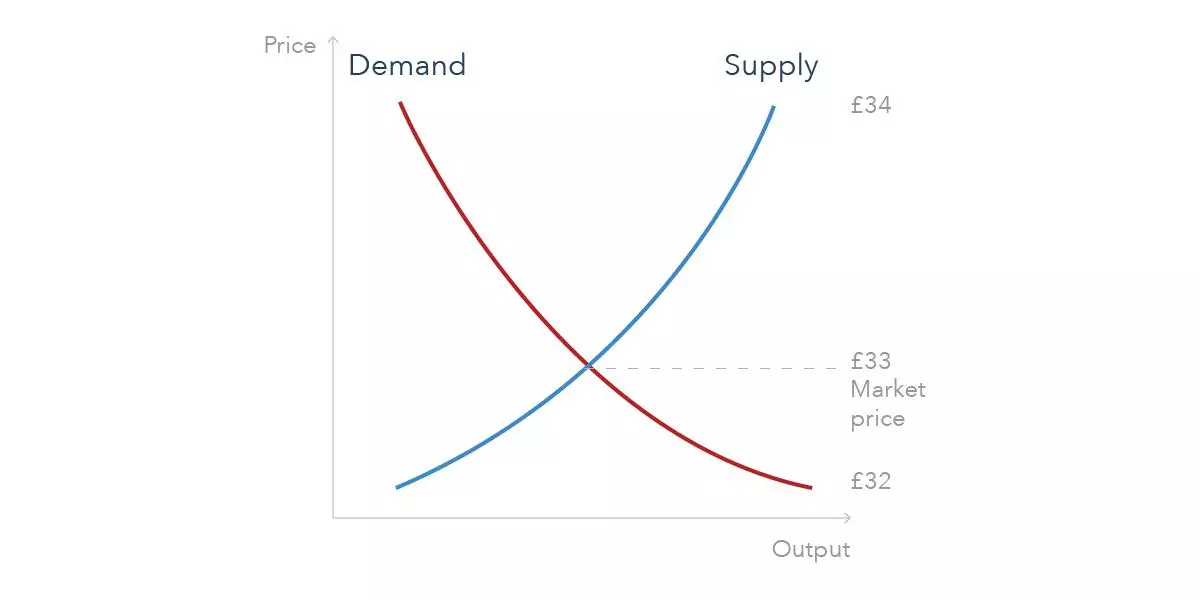
A quote price is the price at which an asset was last traded. It is often defined as the point where supply meets demand, as it’s the price that buyers and sellers agree on.
When trading derivative products, on either side of the quote price (also known as market price) are ‘buy’ and ‘sell’ quotes – also known as the offer and bid prices. These represent the price at which an asset can be bought or sold. The buy price will always be higher than the quote price and the sell price will always be lower.
This differs from investment products where you can choose to buy an asset ‘at quote’.
Learn how CFD trading works
Discover how CFDs prices are quoted and much more in our one-page guide.
How does a quote price work?
Each time an asset is traded, its quote price gets updated. The current price of most assets will be the same as the quote price and will change throughout the day as the asset is bought and sold on exchanges or over the counter.
The quote price is determined by the interaction between buyers and sellers. The more trading activity, the more price movement there is likely to be throughout the day. If there is little trading volume, there will be little to no change in the quote price.
Both parties may change the price during the bid and offer process. As sellers sell the asset, and supply increases, the quote price will go down. As buyers purchase the asset, decreasing supply, the price will go up.
Remember that if there is constant demand and a limited supply, the asset’s price will rise. If the supply is constant but there is little demand, the asset’s price will drop.
Example of a quote price
Let’s say a buyer is willing to pay £32.00 for a share but a seller wants to sell their shareholding for £34.00. The quote price is determined by the price at which the buyers and sellers agree to exchange the stock for. In this case, they might compromise in the middle and the quote price becomes £33.00.
Why is the quote price important to traders?
The quote price is important to traders because it tells them what price an asset is being traded at. Even though it does not provide a lot of detail, it does give them a basic idea of how the market is performing.
By studying historical quote prices and doing thorough technical analysis, you can gain some insight into trends and volatility. This may be helpful in drafting a trading plan and risk management strategy, as well as gaining insight into the efficiency of the market.
Build your trading knowledge
Discover how to trade with IG Academy, using our series of interactive courses, webinars and seminars.