What’s on this page?
What are oil CFDs?
Oil CFDs are contracts used to exchange the difference in value of the oil price between the point at which the contract is opened to when it’s closed. Trading oil CFDs will enable you to speculate on both the rise and fall of the underlying asset’s price movement without taking ownership of it.
CFDs are leveraged derivatives, which means you’ll get exposure to the full value of the underlying oil market by only paying a deposit – called margin. For instance, with leverage, if you wanted to open a position worth $1000, you’d only need to put down $200, which is equivalent to a 20% margin.
Essentials of trading oil CFDs
Oil CFDs are popular among individuals who want to trade oil markets without having to buy and own physical barrels of the commodity. You can go long (‘buy’) or short (‘sell’) on the rise and fall of the oil markets.
You’ll make profits if the markets favour the direction of your trade, however, you’ll make a loss if the markets turn against you. Oil CFDs are also a preferred option for you if you’re looking to make short-term trades.
You can trade oil CFDs on our award-winning platform1 at an average execution speed of 0.014 seconds.
1. All oil CFDs are traded using leverage
You can trade oil using leveraged derivatives like CFDs, which enable you to speculate on the oil market price movement without taking ownership of the underlying asset.
When trading oil CFDs using leverage and you’d like to open a position, you'll be expected to pay an initial deposit that’s a percentage of the full value of the underlying market. Note that leverage may magnify your profits, but it’ll also result in your losses exceeding the initial margin.
It's important to manage your risk carefully and to ensure you’re not staking more than you’re willing to lose.
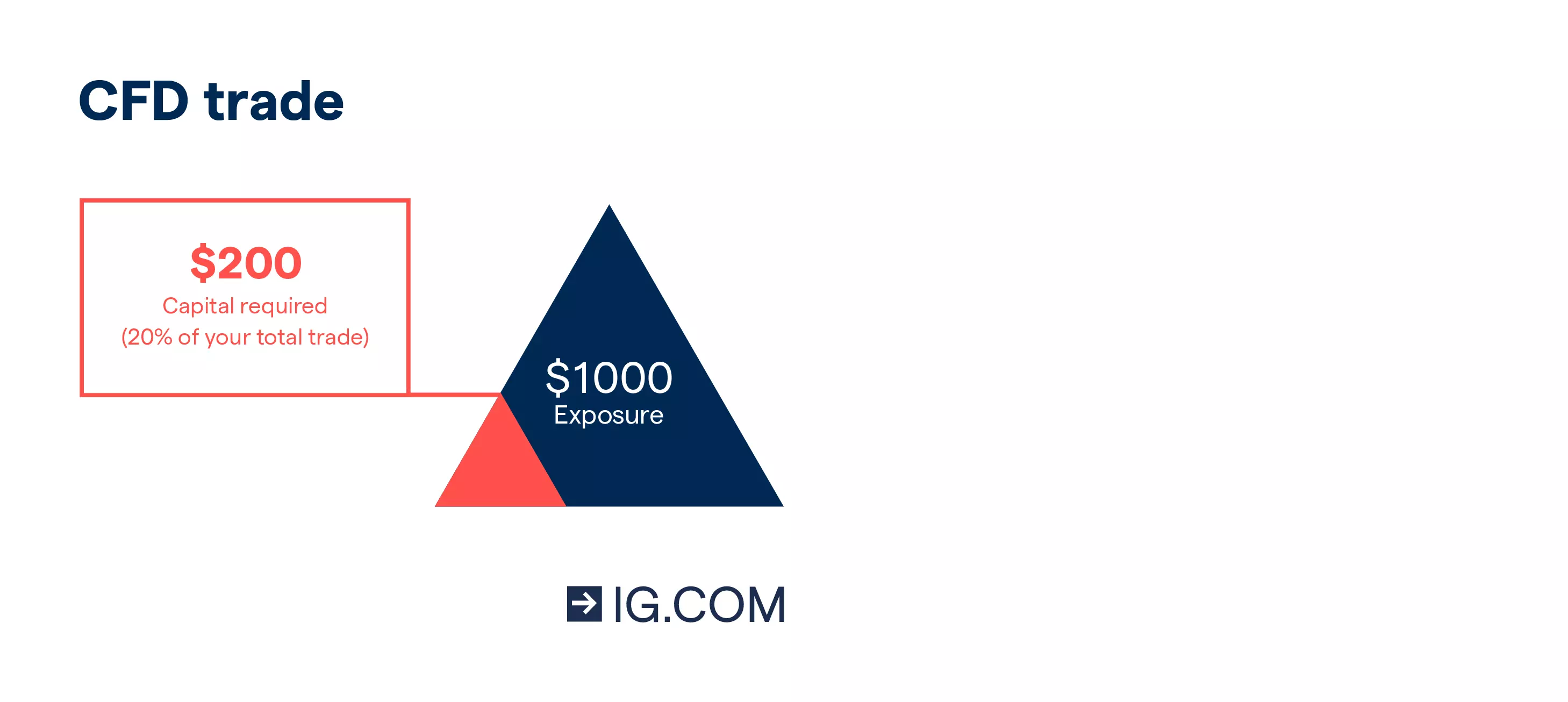
2. You can go long or short with oil CFDs
When trading oil CFDs you’ll go long (‘buy’) if you think the market’s oil price movement will rise and go short (‘sell’) if you believe it’ll fall. This can be done with just a click of a button when you trade CFDs on our award-winning platform.1
3. You can hedge with oil CFDs
Oil CFDs can be used for hedging to reduce the risk that comes with any losses against profits. When hedging, you might decide to open two positions that directly offset each other, which means when the one makes a loss or gain it offsets the change in value of the other.
Note that when hedging you’ll incur costs, be sure to factor these into your hedge calculations and projections.

4. Trading oil CFDs vs other alternatives
CFD trading is one way to get exposure to oil using leverage.
Note that CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage, it’s important that you understand how they work before trading them and if you can afford to lose your money.
If you'd rather not trade with leverage, you can opt to buy and own shares in oil companies or shares in exchange-traded funds that represent oil through share trading. With us, you can buy and hold shares until they appreciate then sell them at a profit. Since share trading doesn’t use leverage, you’ll be liable to pay the full value of your position upfront.
5. Oil CFDs: undated (spot) vs futures vs options
Most people trade oil CFDs using the spot market – sometimes called the undated or cash market. The spot market uses real-time trading oil prices with lower spreads, making it popular among day traders.
Oil futures can be kept open for longer because they don’t have overnight fees. Oil futures are financial contracts in which a buyer and a seller agree to trade a specified number of barrels of oil at a fixed price set for a future date However, remember that they have larger spreads.
Oil options give you the right to buy or sell the market before the commodity reaches its expiry on a specific date in the future. With options, you won’t be obligated to buy or sell the oil market, so if it moves against you, you’d decide to pay only the initial margin you used to open the position.
How to trade oil CFDs
- Fill in a simple form
We'll ask you about your trading knowledge to ensure you understand the risks involved in trading CFDs with us. - Get instant verification
We’ll verify your identity almost immediately. - Fund and start trading
Deposit funds into your CFD account. You can withdraw it whenever you want to.
If you need to build more confidence in your trading skills, open a free demo account with us. You can practise using $20,000 in virtual funds.
1. Learn all about CFDs and oil trading
Oil trading using CFDs involves speculating on the rise and fall of the market price of the underlying asset.
To learn more about how to trade oil via CFDs, enrol for a free course on IG Academy.
Applying for a live account takes just minutes. You’ll fill in an online form and once the application is complete, you’ll receive a notification when it’s accepted. Note that there’s no obligation to fund your account once opened, and you can wait until you’re ready to place your first trade.
2. Open and fund your live CFD trading account
We offer over-the-counter trading for oil markets on our award-winning platform using CFDs on oil spot markets, oil futures and oil options.1 When you open a CFD account with us, there’s no minimum deposit. You can also make withdrawals fast and at no cost to you.
The deep liquidity on our platform offers fast execution with orders being filled on average at 0.014 seconds. You’ll also receive support 24/7 per week by telephone, email and Twitter.2
3. Choose the oil market you want to trade
There are two dominant oil markets for you to trade – Brent Crude and West Texas Intermediary (WTI) also known as US Crude. Brent crude is extracted from oil fields in Europe’s North Sea, while WTI is mined in North America.
Brent crude is the benchmark when trading oil contracts, futures and derivatives at an international level. While in North America WTI is used as a benchmark.
The price difference between the oil markets is based on the commodities’ varying properties. Both Brent crude and US crude are light in nature and can be easily refined and processed by petrol manufacturers.
Live oil and oil-linked prices
4. Decide whether you want to trade undated (spot), futures or options
When you trade the oil markets you have a choice to either trade CFDs on the oil spot price, futures or options. When trading CFDs on the oil spot market you would need to pay for overnight funding. This can be avoided by opening longer-term positions on the underlying oil market by trading futures or options.
5. Open your first CFD trade on oil
You can open your first CFD trade on oil by clicking the commodities section in the top left toolbar of our trading platform. This will display a list of financial instruments in the energies sector. You can then choose the oil market you’d like to trade.
Once this is done, open the deal ticket then, buy or sell your oil market of choice. Go long if you believe the oil market price will increase and go short if you think it will fall.
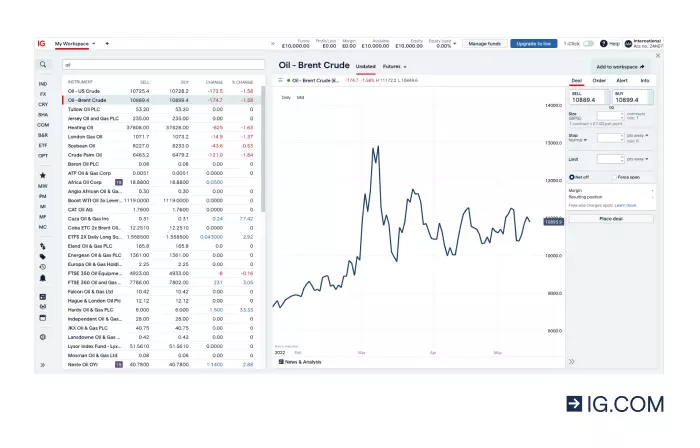
You can set the size of the position you'd like to place on your deal ticket. This will calculate the amount you must pay for the initial margin so you can get exposure to the underlying oil market.
With us, you’ll get trading alerts when the oil market price moves some points above or below the level you’ve set. Note that despite setting these alerts, it remains your main responsibility to monitor your position. It’s important to also use our tools to manage your risk carefully.
To gain access to a list of markets that have 'buy' and 'sell' suggestions from our trading signals, click on 'signals' in the bottom left toolbar of our platform. These suggestions are based on emerging chart patterns and key levels that’ve been met.3
When making your trading decisions, remember not to solely rely on third-party-generated chart patterns on our platform. Conduct your own due diligence using technical and fundamental analysis.
6. Monitor your position
Once you've opened your position using your CFD trading account, you can set your signals and alerts, and monitor your position Our award-winning platform will also enable you to see the running profits and losses made on your open position.1
What affects the price of oil?
The demand and supply of oil, as well as various macroeconomic trends, tend to affect the oil market prices. Here are some examples of what affects the price of oil:
- Controlling the global oil supply. Only five countries produce about half of the world’s oil in total, which increases their power and sovereignty to control the global oil supply. This directly impacts the oil price since the handful of countries can manipulate it
- Driving global oil demand through growing economies. Positive performance in global economies increases oil demand. When global economies grow exponentially, it increases the oil price. However, weakening global economies decrease oil demand and its price
- Geopolitics at play. When war or conflict erupts in oil-producing regions, this impacts its supply. This, in turn, increases the volatility of oil and its price within the market
Try these next
Seize the opportunity to trade on our easy-to-use platforms and apps
Watch market developments in real-time using charts generated by fast cutting-edge technology
Learn how to trade online and access key markets using our award-winning platform1
1 Best Finance App, Best Multi-Platform Provider, Best Platform for the Active Trader and Best Online Stockbroker as awarded at the ADVFN International Financial Awards 2025.
2 Available 24/7 except from 7am to 5pm Saturdays (AEST). Our trading hours are based on UK hours, and are converted to AU time zones. This means that the times listed are affected by both UK and AU clock changes in the year, and will be adjusted by +/- 1 hour accordingly.
3 Our signal service does not constitute and shouldn’t be regarded as investment advice. We provide an execution-only service. You act on signals entirely at your own risk.
